The automated business process systems that (since the 1990s) have collectively been known as enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions are now fundamental to businesses operating in diverse industries; this includes energy, semiconductors, manufacturing, maintenance, materials management, retail, media and communications. What we now know as ERP evolved from early materials requirements planning (MRP) software (developed in the 1960s) to help manufacturers better manage production and sales processes. In the 2000s, when ERP programs moved from company servers to cloud-based environments, digital transformation was fueled by innovative, intelligent technologies that offered more sophisticated automation and reporting capabilities, as well as a greater array of real-time business to business (B2B) integrations. Today, many privately-owned companies and global organizations rely on ERP systems from Oracle, SAP (News - Alert), Microsoft, Sage, SYSPRO, and others to improve efficiency and productivity in every department, from procurement and supply chain/logistics to human resources and finance.
Despite the vast functionality of modern ERP applications, automating sales processes continues to be a core component of many systems. ERP vendors typically offer a proprietary version of an Order Management (OM) system that businesses use to capture the details of customers’ orders (i.e. demand), and automatically manage the pipeline of parts or supplies that will be required to fulfill incoming orders. Among the individual information processed for each order, OM systems generally include standard fields for Customer, Ship To address, Bill To address, Product (with pricing details), Order Quantity, Scheduled Ship Date (SSD), Promised Ship Date, Customer Requested Date (CRD) and Scheduled Arrival Date (SAD). Additional attribute fields may display on customer-facing documents, such as Sales Order Acknowledgements and/or Invoices that provide details about fees and goods deliveries.
OM systems often leverage visual builder cloud services (VBCS) and integration cloud services (IC) through a customized user interface (UI) that enables programs to read data and communicate electronically in real-time with suppliers. Based on this data, shipment dates fields are auto-populated according to product availability and associated rules that define parameters for managing supplies against sales orders.
The problem:
These automated systems work well—until the customer requests sales order changes after the order is in process. When this happens, the various dates may need to be updated manually by an employee, who must then query each order individually, or prepare a batch file reflecting information necessary to interface via middleware with the order revisions. Depending on the quantity of data associated with an order, it could take the employee five minutes to update just one order.
This situation becomes exponentially more time-consuming for mass orders and/or when the customer is a reseller who may be ordering many thousands of goods on a weekly basis, with demands for varying delivery dates and locations. For example, in my nearly two decades as an ERP cloud strategy architect (specializing in Oracle (News - Alert) business management and operational solutions), I have seen cases in which customer sales orders of approximately 25,000 per week required manual updates to ten percent of the total weekly order. With no automated solution, making these manual order revisions can tie up employees for more than 200 tedious hours per mass order.
The solution:
Recognizing how this problem was costing a global energy customer time and money, I developed a new Sales Order Dates Update tool to facilitate mass updates for their sales order transactions, eliminating the need to manually update each order independently. While this new tool was created to integrate with the Oracle Cloud OM system, it is conceptually consistent with other ERP systems, and other businesses may find this prototype design and deployment guidance helpful in re-engineering their own customized solutions for .
When an ERP system’s out-of-the box UI functionality does not support mass updates to OM system fields (such as Scheduled Ship Date, Promised Ship Date, Customer Requested Date, or Scheduled Arrival Date), the impact may ripple through downstream parts/supplier planning or upstream distribution channels. Customers also expect that (regardless of changes), every business user or customer service representative (CSR (News - Alert)) should have the ability to query orders across business entities, create mass updates to order dates, and generate notifications showing the date status for updated sales order transactions.
The advantage of the Sales Order Dates Update tool is that instead of spending three to five minutes to manually update one sales order, with this tool a user can make mass updates to 1,000 sales orders in the same five minutes and meet clients’ and suppliers’ communication expectations. For my global energy client, upon implementation, a user job role was defined to control tool accessibility, incorporating factors related to data access and security. Although the tool was initially designed for the company’s U.S. operations, after experiencing the efficiencies gained through its robust mass update capabilities, the client is now planning a roll-out for its other regional geographies.
Design and implementation:
Since this tool was designed for Oracle’s ERP platform, it was built with the vendor’s recommended VBCS and Oracle Integrated Cloud (OIC) functionalities, which enable business users and CSRs to query sales orders in bulk using the warehouse management system (WMS), various OM system date fields, and other source system data.
Figure 1 illustrates the tool’s process flow, depicting the integration between the Cloud OM system and the VBCS/OIC to manage mass updates of sales order dates. As seen in the flow chart, the tool contains search parameters in multiple fields, and displays sales order search results with existing Scheduled Ship, Promised Ship, Customer Requested, or Scheduled Arrival dates, where business users can review the data and make changes as per the customer’s requirements. The tool’s search results section displays eligible sales order lines, and allows users to export the displayed search results to a local device to make necessary date field updates in a CSV file format (before uploading the updated data). The upload function then reads the updated file data and processes the records in the OM system, using recommended application programming interfaces (APIs) via OIC services. Post-processing the updated file data in the Cloud OM system, OIC services will automatically send an email notification with the updated status of each line processed through the OM system.
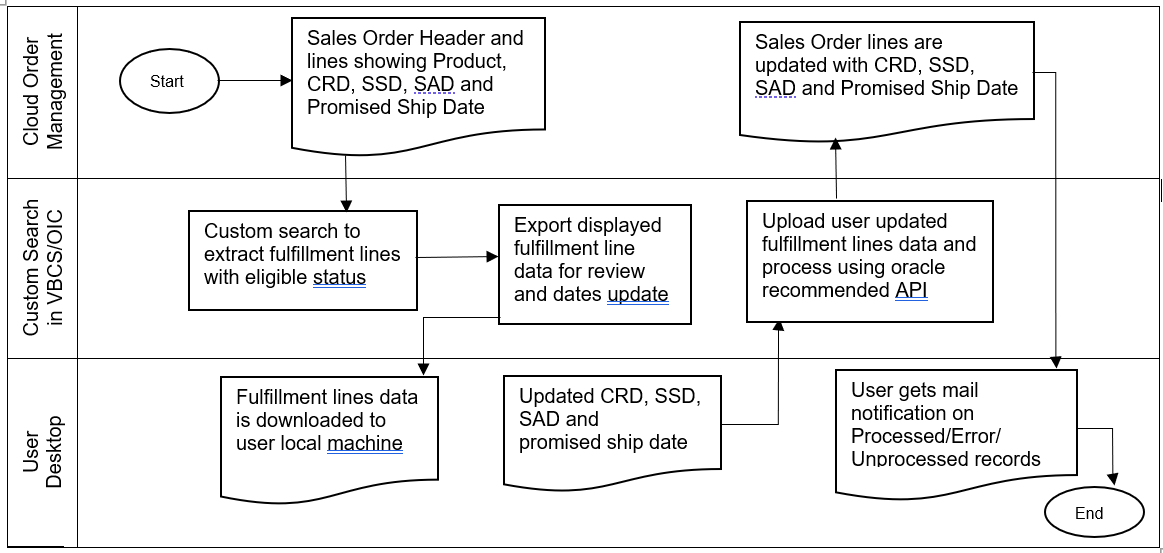
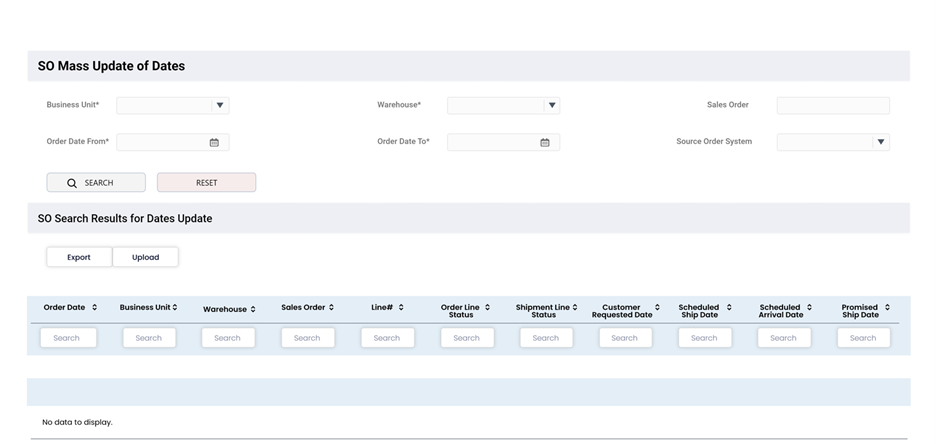
Figure 2 represents the data fields and search parameters that can be reviewed and updated for eligible sales orders. Importantly, a user/CSR making mass updates with the tool does not necessarily need to access the OM system screens, where data is accessible only by users with specific job roles. The tool has been designed to allow a business user or CSR to query the sales order and make a customer’s updates without having visibility or accessibility to other sensitive data.
In addition to solving for mass sales order updates, the tool offers functionality for bulk cancellations of sales orders. Without the automated tool, whether a customer cancels an entire order or just a few products within the order, a business user/CSR would have to manually search the order and process the cancellation. With the tool, bulk cancellation requests are easily automated through the APIs and OIC services, and automatically confirmed with an email notification.
The Sales Order Dates Update tool also enables users to upload ad hoc file data containing mass volumes of order lines (i.e. 20,000-25,000) in under 10 minutes.
Saving employee hours and reducing the tedium associated with manual updates is of great value to businesses of any size, as is the ability to meet dynamic customer demands. Given current economic and manufacturing pressures on global supply chains, the tool’s effectiveness in quickly capturing, processing, and communicating schedule changes up and down the production stream may be of even greater value, as this operational efficiency contributes to productivity and profitability.

About the author: Prabhakara Srinivas Malladi is Associate Director of SPL Consulting, Inc., a global business solution and ERP systems provider. Since launching his career at Oracle and IBM (News - Alert) nearly two decades ago, developing innovative systems for supply chain and manufacturing industries, Mr. Malladi has specialized in designing and implementing Oracle Cloud-based technologies and sophisticated integrated applications for global organizations in energy and other industries.
Edited by Alex Passett